
If the aperature is much larger than the wavelength, there is not much diffraction, and only the edges of the wavefronts bend slightly. If the aperature is around the size of the wavelength, or smaller, the waves spread out on the other side of the obstacle as if originating from a point souce in the aperature. Waves always bend around an aperature, however, the amount of diffraction depends on whether the aperature size is large or small compared to the wavelength. When a wave encounters a barrier with a small aperature, relative to its wavelength, it bends/diffracts and spreads out in a circular wave. When a beam of particles encounters a barrier, it either is stopped by the barrier, or passes through the aperature cleanly without any change in direction This is the reason why viruses cannot be observed under a light microscope as its size is shorter than wave length of visible incident light.The bending of waves around corners that occurs when a portion of a wavefront is cut off by a barrier or obstacle. It will be diffracted around the obstacle. Having a wavelength more than that of the obstacle, it is impossible to retrieve any information about the obstacle because it will not be reflected back. Another implication while considering diffraction is that if the waves are A superior quality sound proofing means that there are no openings present, as even a small aperture can let sound enter the room and by the process of diffraction can spread in the whole area and cause disturbance. This principle is also used while soundproofing a room. The long wavelength waves can bend around obstacles and reach our ears from sources situated at distant places.

#Diffraction of a wave crack#
The thunders which are nearer to us are audible as a sharp crack which shows the presence of a number of high frequency sounds, whereas, distant thunders are heard as a low rumble due to presence of longer wavelengths. This process can also be observed during thunderstorms. It means that we will be able to hear low frequencies around obstacles better than frequencies which are higher. Important thing to keep in mind with regard to diffraction of sound waves is that it is more pronounced with waves of longer wavelength. This duality of diffraction has many applications. Due to this reason, the same sound wave can bend around obstacles and also tend to disperse in different directions after passing through a hole or crevice. Diffraction can also be said to have a dual nature. In fact, one can hear sounds around barriers and corners through a process that involves both reflection and diffraction.
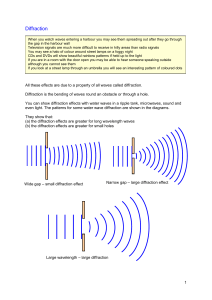
Thus, diffraction is the cause of violation of law of linear propagation of light or sound.ĭo you think it would be impossible to hear a sound if sound waves could not be diffracted? In some instances, the answer would be yes and in others the answer may be no.

Same thing happens in case of light also but the level of diffraction in light is very small. After diffraction through a small hole, the sound is reaching the receiver. Sound from a source which is placed behind the screen / wall is creating sound waves. In the figure above, we see a receiver standing on the other side of a wall/ screen. Hearing voice while beings far apart from source is an example of diffraction of sound waves. It is due to process of diffraction that we are able to see/hear certain things which would not have been possible otherwise. Diffraction describes the movement in wave’s direction as it bends around an obstacle. Bending from one medium to the other medium, reflection off surfaces, and travelling through objects are some of the properties that waves possess. We can see this process in both light and sound waves. Diffraction is a phenomenon that we experience in our day to day life.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
